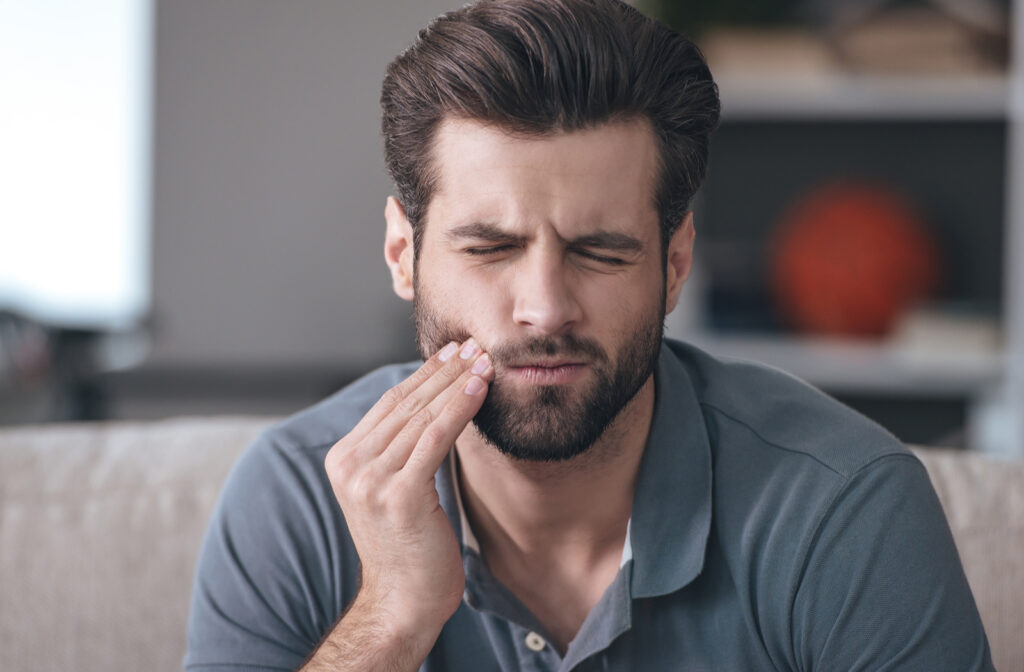
In many situations, tooth pain can be a minor nuisance, but sometimes it can mean something more significant. If you have tooth pain, how do you know when to visit your dentist for an examination?
Continue reading to learn more about tooth pain, including when to see your dentist and what conditions it can be a symptom of.
What Is Tooth Pain?
Tooth pain, better known as toothache, can occur for many reasons. You may experience discomfort when a piece of food is stuck in your gums or due to a significant problem, like a broken tooth. You can experience a minor or severe toothache, depending on the cause of your pain.
Tooth Pain Symptoms
You may experience several symptoms of a toothache depending on its severity. Some common signs of a toothache include:
- Pain when chewing in your teeth or jaw
- Headache
- Sensitivity to hot & cold temperatures
- Blood or discharge around a tooth
- Jaw swelling
- Bad breath
- Fever
- Bad taste within your mouth
- Swollen glands
While all of these symptoms can mean you have a toothache, how do you know when to visit your dentist?
When Should You Visit Your Dentist for Tooth Pain?
It can be hard to know when tooth pain is severe enough to warrant a trip to your dentist’s office. You must receive treatment if you have a significant problem—dental infections can spread to other parts of your face or even your bloodstream.
Visit your dentist as soon as you can if your tooth pain:
- Lasts longer than 2 days
- Is severe
- Presents alongside fever, earache, or pain when opening your mouth
Your dentist can perform a physical exam to look for signs of any dental problems. After diagnosing the underlying cause of your pain, they can provide effective treatment to relieve your symptoms.
What Can Tooth Pain Be a Symptom of?
While tooth pain can occur due to a minor problem, it is a symptom of several dental issues. If left untreated, these conditions can cause significant health problems. A toothache may mean you’re experiencing tooth decay, an abscessed tooth, a tooth fracture, or bruxism.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is also known as a cavity. A cavity is a damaged area within the hard surface of your tooth, creating a small hole. This decay happens when bacteria feed off of the sugars and starches within your mouth, creating plaque.
Plaque removes your tooth’s enamel, creating tiny holes within the tooth. As tooth decay progresses, bacteria drill deeper into the tooth until infection occurs. Without treatment, a cavity can damage a tooth or cause an abscess to develop.
Symptoms of tooth decay include:
- Toothache
- Tooth sensitivity
- Pain when eating or drinking
- Visible holes in the teeth
- Brown, black, or white staining on the tooth
- Pain when biting down
Abscessed Tooth
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus that develops due to a bacterial infection. Abscesses occur when bacteria enter the dental pulp, the inner part of the tooth containing blood vessels, nerves, and other connective tissue. You may develop a tooth abscess if a cavity is left untreated for a long time.
A tooth abscess is a significant problem that won’t go away without treatment. If ignored, you run the risk of a ruptured abscess that can spread to other parts of the body, potentially causing sepsis.
Symptoms of a tooth abscess include:
- Severe toothache
- Sensitivity to hot & cold temperatures
- Sensitivity to pressure
- Fever
- Swollen face or cheeks
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
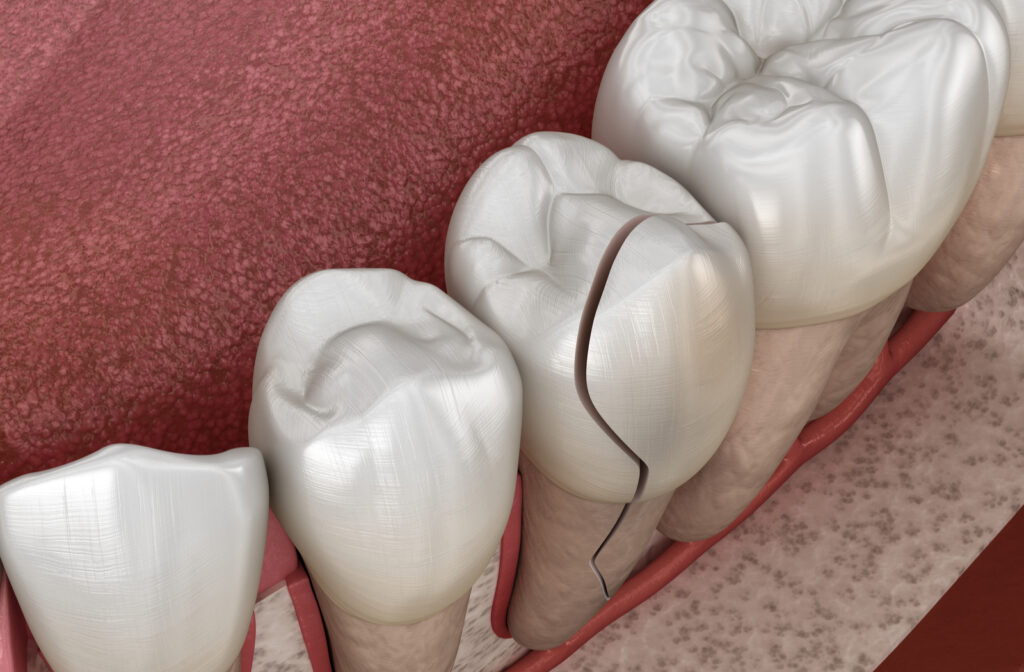
Tooth Fracture
A tooth fracture occurs when there is a crack within the tooth. This fracture can be minor, or it may cause your tooth to break or split. Your tooth can fracture for several reasons, including:
- Age
- Biting hard foods
- Bad chewing habits
- Large dental fillings or root canals
- Teeth grinding
- Physical trauma
Treatment for a fractured tooth can include bonding the tooth, receiving a dental crown, a root canal, or tooth extraction is necessary. If left untreated, a broken tooth is at risk of developing a bacterial infection.
Symptoms of a fractured tooth include:
- Pain when chewing or biting
- Sensitivity to heat & cold
- Pain
- Swollen gums
Bruxism
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, is a condition where you grind or clench your teeth. You may clench your teeth unconsciously during the day or grind your teeth at night while you sleep.
While mild bruxism may not affect your oral health, more severe forms of this condition can cause complications. These complications include damage to your teeth and tension headaches.
Symptoms of bruxism include:
- Chipped, flattened, or loose teeth
- Worn tooth enamel
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Jaw pain
- Tired or tight jaw muscles
Know When to Seek Help
Tooth pain can seem insignificant, but you should never ignore it. Even if there are no problems, you can ensure that you aren’t at risk of further complications. A visit to your dentist can help protect your oral health.
Contact your dentist if you’re experiencing tooth pain.